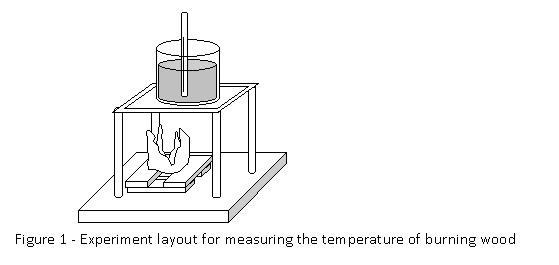
Hypothesis
The hardwoods are denser and therefore produce more heat compared to soft wood.
Overview
Firewood
There are many types of firewood available for use in cooking or heating. The choice of wood to be used depends the purpose for which it is used, and weather conditions. Your choice of wood may vary if it is used for outdoor cooking, barbecques, fire places or campfire. Some of the things we need to know about firewood are listed below.
Use only dry or seasoned firewood for burning. Wet or recently cut firewood will contain water moisture. They will burn at lower temperatures and release more smoke.
The amount of heat from a burning wood is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs). Hard woods have higher BTUs and therefore are more effective as firewood, as compared to soft woods which have lower BTUs
Hard woods have a very high density. The amount of potential thermal energy stored per unit volume of hardwood is high and therefore hardwoods have higher BTUs. These woods are difficult to ignite but once they start burning, they will burn for a longer period of time, giving out less intense heat.
Soft woods have a lower density. The amount of potential thermal energy stored per unit volume of hardwood is low and therefore soft woods have lower BTUs. These woods are easy to ignite but the heat is low and they do not burn for very long.
Scientific Terms
British Thermal Units (BTUs), density, thermal energy
Conclusion
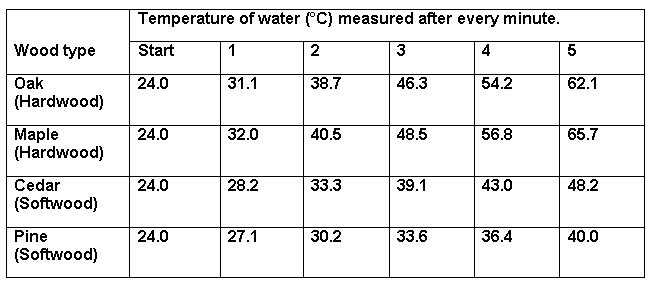
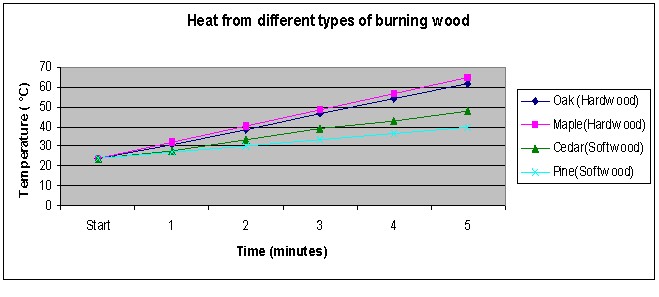
The hypothesis that hardwoods produce more heat as compared to soft wood is proven to be true. The hardwood gave out more heat when burned, thus driving up the temperature of the water higher than in the case of softwoods. In addition, they burned for a longer period of time as compared to the soft wood.
With the rising prices of electrical heating, oil and gas, the use of firewood for burning is an alternative source of cheaper energy. However overuse of firewood for burning will lead to pollution and deforestation. In addition, the carbon dioxide gases released into the atmosphere from an open fire contribute to global warming and ocean acidification.
Also consider
The experiment can be repeated by measuring the amount of time taken for the wood to burn out.
Try to repeat the experiment using an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature of the fire directly.
Try using a different formation of the wood pieces for burning. Would the results be different?
Related videos
Hey there! Here are some awesome videos about this science project that we think you'll really like. They're not only super fun, but they'll also help you learn more about the science behind the project. So sit back, relax, and get ready to have some fun!!