| Complexity level: | 6 |
| Project cost ($): | 20 |
| Time required: | 1 hour to prepare, 1 hour for the science project experiment |
| Material availability: | A car with PVC seats and another with leather seats, are required |
| Safety concerns: | Ensure that this experiment is conducted ina well ventilated, safe place, with no flammable substances /gases present. |
Hypothesis
Compared to PVC seats, leather car seats produce more static electricity than PVC seats. Our second hypothesis is that between cotton, polyester, nylon, and human hair - polyester will produce the greatest static charge.
Overview
Static Electricity
Static electricity is created by the accumulation of electric charges on the surface of a body. The accumulated charges will be discharged when contact is made with another surface.
All matter is made up of atoms. The atom has a nucleus in its core, which contains neutrons and protons. Its electrons are located outside the nucleus. The ability of the atom to capture or release its electrons is determined by its position in the tribo-electric series. When an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged and it will fall on the positive side of the tribo-electric series. When the atom captures an electron, it will be negatively charged and will fall on the negative side of the tribo-electric series.
When two types of insulating materials are rubbed together, static electric charges will be produced. The friction created by the rubbing of these two materials will help to produce static electricity. One of the materials will release electrons while the other will receive the electrons.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science fair project:
- 1 balloon
- 1 copper plate 200mm x 300mm
- 1 ground connection
- 1 jumper wire with crocodile clips at both ends
- 1 PVC car seat
- 1 leather car seat
- 1 polyester cloth
- 1 cotton cloth
- 1 nylon cloth
- 1 wig (human hair)
- a flat tray
- 1 ruler
- 1 large sheet of paper
- 1 paper knife
Procedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the type of materials tested – namely PVC and leather car seats, against cotton, polyester, nylon and hair. The dependent variable is the number of paper pieces picked up by the balloon. The constants (control variables) are the size of the balloon, the number of times the balloon is rubbed on the material tested, the direction of rubbing, and the weight of the paper bits.
2. The copper plate is grounded by connecting the jumper wire to the ground connection.
3. 200 pieces of paper measuring 5mm by 5mm are cut out from the same sheet of paper. The pieces of paper are discharged from all electrical charges, by placing them on the grounded copper plate. They are then transferred to the flat tray.
4. The inflated balloon is discharged by rolling it over the grounded copper plate.
5. The science project experiment is started by rubbing the balloon on the cotton cloth 5 times. The pieces of paper are placed on the PVC car seat. The balloon is then used to pick up the paper pieces from the car seat. The number of paper pieces picked up by the balloon is counted and recorded. The paper pieces are discharged on the copper plate and returned to the tray.
6. The balloon is also discharged by rubbing it on the grounded copper plate. Procedure 5 is repeated by placing the paper on the leather car seat. The number of paper pieces collected by the balloon rubbed with the cotton cloth is recorded in the table given below.
7. Repeat procedures 5 and 6 by rubbing the balloon 5 times over the polyester cloth, nylon cloth and hair sample. Carefully record all your findings.
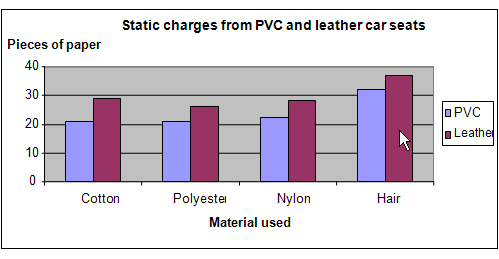
Results
The results showed that the balloon rubbed against the hair collected the most number paper pieces from the PVC car seat as well as the leather seat. Between the two seats, the balloon picked up more pieces of paper from the leather seat.
|
Car seat material |
Number of pieces of paper picked up |
|||
|
Cotton |
Polyester |
Nylon |
Hair |
|
|
PVC |
21 |
21 |
22 |
32 |
|
Leather |
29 |
26 |
28 |
37 |
Conclusion
Our hypothesis that leather car seats produce more static electricity compared to PVC seats is proven to be true. Our second hypothesis has been proven false, as between cotton, polyester , nylon and human hair, the human hair produced the highest charge.
The static charge present on surfaces is higher during periods of low humidity. They pose a great danger at gas stations where flammable gases are constantly present. A sudden spark caused by the rubbing of a person’s clothing against the car seat while the person gets out of the car could be extremely disastrous.
Also consider
The science fair project can perhaps be repeated, using a comb instead of a balloon.
Would different car seat materials (eg. seats made from cloth or Vinyl) produce different results?
References
Static electricity - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_electricity
Static electricity - http://science.howstuffworks.com/vdg1.htm

