Hypothesis
Sea water with higher salinity will conduct more electricity.
Overview
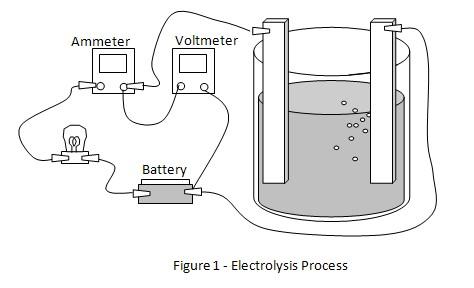
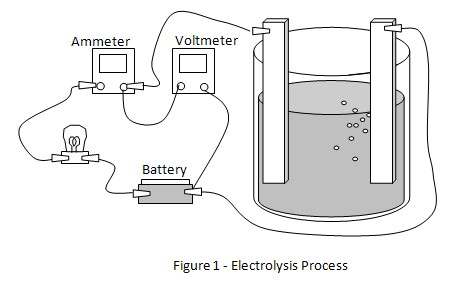
Electrolysis process
Electrolysis is the process where electric current passes through a solution. The process requires a voltage source, an anode (positive) electrode, a cathode (negative) electrode and an electrolyte solution.
The electrolysis process will start when the positive terminal of a battery is connected to the anode and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the cathode. When this connection is done, the positive ions in the electrolyte will move towards the cathode and the negative ions will move towards the anode resulting in current flow.
Water by itself is a poor conductor. But if salt or sodium chloride is added to water, it can start to conduct electricity through the electrolysis process.
Sodium chloride in solid form does not conduct electricity. The electrostatic attraction between the sodium ion and chloride ion is very strong when it is in solid form. However when sodium chloride is mixed in water, the sodium and chloride ions are separated and move freely in the solution making it a good electrolyte.
Scientific Terms
Electrolysis, electrolyte, ions, electrodes, anode, cathode, sodium chloride
Conclusion
The hypothesis that sea water with a higher salinity will conduct more electricity is proven to be true. The presence of salt in seawater makes it a good conductor.
Electrolysis process can be used to store energy and reproduce it for later use. Examples are the rechargeable and disposable batteries and batteries used to start cars. Currently environment friendly energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines make use of batteries to store the energy that they produce for later use.
Also consider
The experiment can also be done by varying the amount of salt in the water.
This experiment can also be repeated to observe the effect of different sizes and types of electrodes.
References
Electrolysis - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrolysis
Electrolysis - http://www.tutorvista.com/content/chemistry/chemistry-iii/redox-reactions/electrolysis.php
Electrolysis - http://www.educationalelectronicsusa.com/c/electrolysis-I.htm
Related videos
Hey there! Here are some awesome videos about this science project that we think you'll really like. They're not only super fun, but they'll also help you learn more about the science behind the project. So sit back, relax, and get ready to have some fun!!