| Complexity level: | 6 |
| Project cost ($): | 20 |
| Time required: | 2 day to prepare, 4 hours for the science project experiment |
| Material availability: | Easily found |
| Safety concerns: | Basic safety requirements. |
Hypothesis
Between Sand, clay and silt soil, silt retains the most water.
Overview
Soil water retention
Soil consists of particles of rock and decaying organic materials. Soil is important for the growth of plants because it supplies them with water and the necessary nutrients. Although there may be many types of soil available for use in our gardens, the most common types are sand, clay and silt.
Sandy soil has very coarse grains. This makes it difficult for them to hold water. Therefore sandy soils is dry and very light. The plants planted in sandy soil will need to be watered frequently.
Clay soil is typically very fine-grained and is able to retain water very easily. The water retention properties of clay soil makes it very suitable for dry season planting. However its water drainage properties are very poor.
Silt is typically very rich in nutrients and water. It is considered a very fertile soil. It has very good drainage properties and is also able to retain water.
Between silt and clay, which do think will retain the most amount of water?
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science project experiment:
- 3 plastic pots
- 3 plastic containers
- 3 sheets of fine wire mesh, slightly larger than the size of the cover of the plastic container
- 600 ml of water
- 1 sack of sand
- 1 sack of clay
- 1 sack of silt soil
- 1 weighing machine
- 1 measurement cylinder
- 1 marker pen
Procedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the type of soil used. The dependent variable is the amount of water retained in the soil. This is determined by measuring the water drained using the measuring cylinder and also checking the weight of the pot. The constants (control variables) are the amount of water used, the amount of soil used and the time taken for the water to drain from the soil.
2. The 3 pots are labeled A, B and C. The sand is placed inside pot A up to 20mm from the top. Similarly the clay soil and silt soil are placed in pots B and C up to 20mm from the top of the pot.
3. The pots A, B and C are put outside in the hot sun to dry and for the soil to settle down in the pots for 2 days. After the second day, the weight of the pots is measured and recorded in the table below.
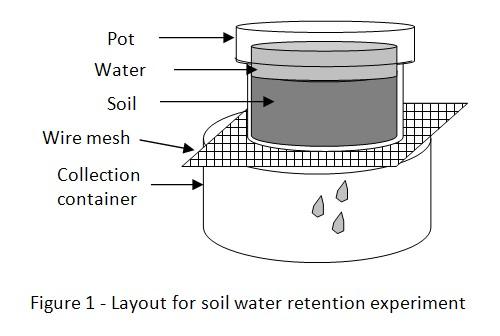
4. The pots A, B and C are placed on the wire mesh and plastic collection container as shown in figure 1. Using the measuring cylinder, 200ml of water is poured into each of the pots and they are allowed to drain for 4 hours.
5. After 4 hours, the amount of water in the collection containers is noted using the measuring cylinder and the weight of pots A, B and C are checked and recorded in the table.
Results
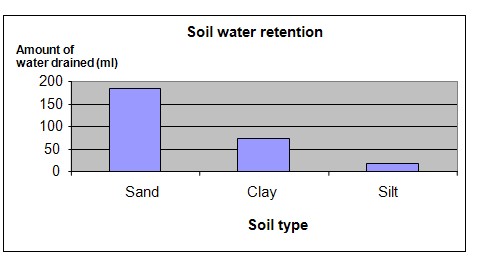
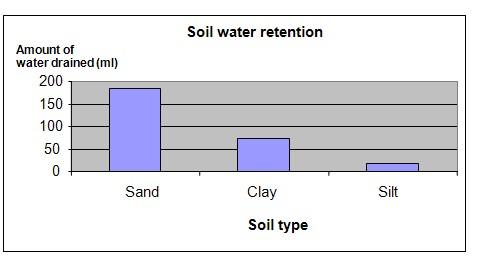
It is observed that pot C with the silt had retained the most water. It had the least amount of water in the collection container and the biggest increase in soil weight. Pot A containing the sand was the poorest in water retention with almost all the water drained into the collection container and showing only a small increase in weight.
|
Soil type |
Initial pot weight (g) |
Final pot weight (g) |
Weight difference (g) |
Amount of water in collection container (ml) |
|
Sand |
1442 |
1456 |
14 |
186 |
|
Clay soil |
1328 |
1454 |
126 |
74 |
|
Silt soil |
1376 |
1559 |
183 |
17 |
The chart below represents the results of our science experiment.

Conclusion
The hypothesis that between clay, sand and silt, silt will retain the most water is proven to be true.
Soil water retention is very important for the continual growth of plants and the survival of the various organisms living in the soil. It also helps reduce soil erosion.
Also consider
What would happen if the science fair project was repeated using mixtures of different soils?
The science fair project can be repeated using different amounts of water and soils from different locations to compare the results.
References
Water retention - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Soil_water_(retention)
Types of soil - http://lifestyle.iloveindia.com/lounge/types-of-soil-3119.html

