| Complexity level: | 2 |
| Time required: | Once preparations are finished, the flowers will sit for at least 24 hours, then conclusions will be made after. |
| Safety concerns: |
Overview
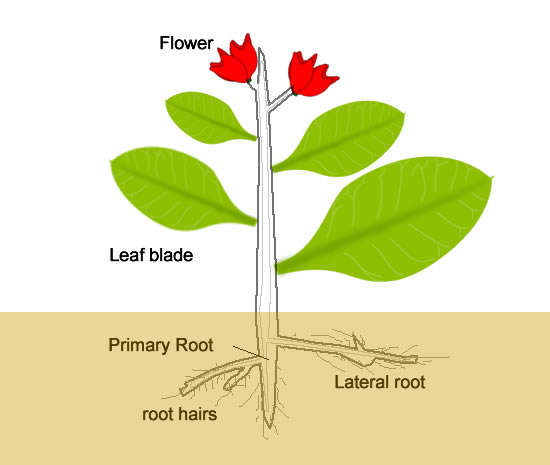
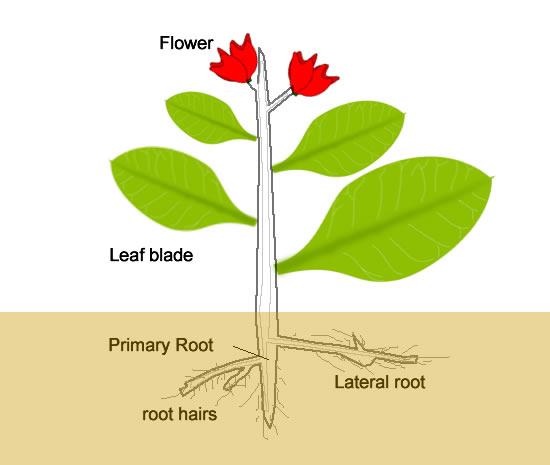
Scientific Terms
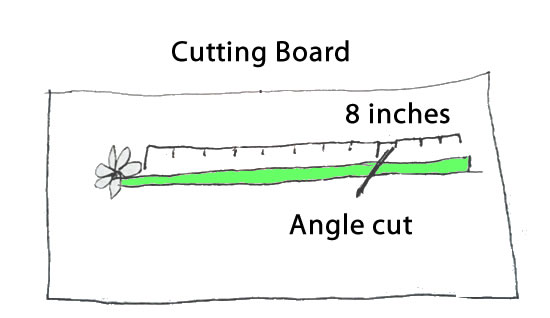
Materials
Kiwi Crate — hands-on STEAM project kits for ages 6–9, delivered monthly. (Affiliate link)
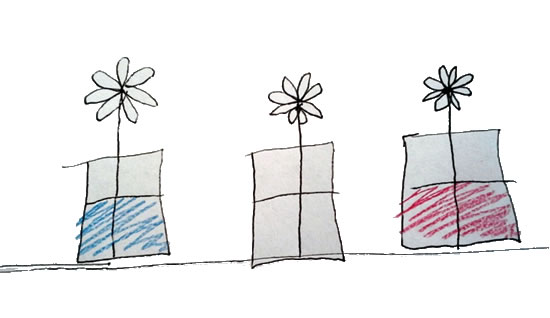
See what’s includedProcedure
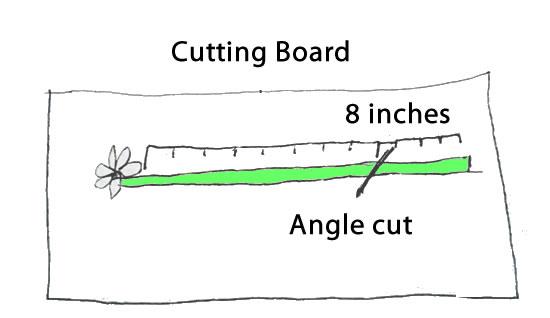
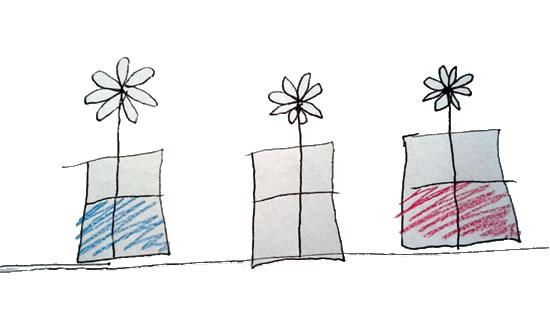
References
Related videos
These videos explain the science behind this project and demonstrate key concepts used in the experiment.
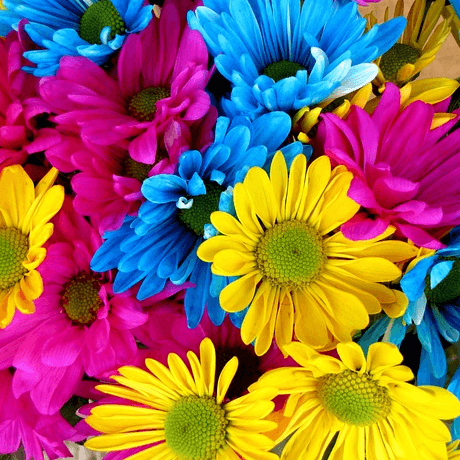
Get ready for some floral fun! Watch as these flowers change colors when placed in different colored water. Want to take it to the next level? Try placing the flower in a different colored water every day and see what happens!
Have you ever seen a rainbow rose? These special blooms have several colors on a single rose, and they're made possible by splitting the stem and soaking in different colored water! If you want to learn how to make your own stunning rainbow roses, be sure to check out this video and follow along with the step-by-step instructions.