| Complexity level: | 5 |
| Project cost ($): | 20 |
| Time required: | 1 hour for preparation, 2 hours for observation |
| Material availability: | Easily found at a hobby store |
| Safety concerns: |
Hypothesis
The LED lamp will require less power to produce the same level of brightness as an incandescent lamp.
Overview
Incandescent lamp versus LED lamp
We use light bulbs everyday to brighten up our homes, dark corridors, streets and many more. Two common types of light bulbs are the incandescent light bulb and the LED light bulb. Both types of light bulbs have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice of which type of light bulb to be used may depend on factors such as cost, lifespan and power consumption.
Incandescent light bulbs produce light by heating a filament. The current that flows through the filament will cause it to become so hot that light will be produced. The filaments are housed in a glass bulb which contains either a vacuum or an inert gas, to prevent the oxidization of the filament. They are very affordable and can be used with alternating currents (AC) or direct currents (DC). Incandescent lamps are used in homes, commercial buildings, automobile lighting, torchlight and many other applications.
LED lamps produce light using light emitting diodes. Normally, the light generated by a single LED bulb will be of a much lower intensity compared to an incandescent lamp. This is the reason why LED lamps will contain many individual LED bulbs to produce the same brightness. LED lamps work on direct currents and therefore need step down and rectifier circuitry to work with an AC power source.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for the science fair project:
- A 60 watt incandescent light bulb
- Socket for the incandescent lamp
- LED bulbs of several wattage ratings (1.5W, 3.0W, 4.5W, 6.0W, 7.5W, 9.0W, 10.5W)
- Socket for the LED bulb
- Electric cables
- 3-pin plugs
- A lux meter
- A ruler
MEL Physics — hands-on physics experiment kits delivered monthly — real experiments, not just reading. (Affiliate link)
See what’s includedProcedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the type of light bulb used – incandescent bulb and LED bulbs. The dependent variable is the brightness of the bulbs. This is determined by measuring the brightness using a lux meter. The constants (control variables) are the distance of the lux meter from the light bulb, the temperature of the room (which will remain at room temperature) and the power rating of the incandescent lamp.
2. Wire the cables and the plug to the incandescent bulb socket and the LED lamp socket. Test the incandescent bulb and the LED bulb before starting this experiment.
3. Place the lux meter 1000mm from the surface of the incandescent lamp. Turn on the incandescent lamp. Measure the luminous intensity indicated in the lux meter. Record the measurement in a table, as shown below.
4. Disconnect the incandescent lamp from the power socket and connect the LED lamp socket. Test the luminous intensity of the 1.5W, 3.0W, 4.5W, 6.0W, 7.5W, 9.0W, and 10.5W LED bulbs by placing the lux meter 1 meter from the surface. Record the measured reading in a table, as shown below.
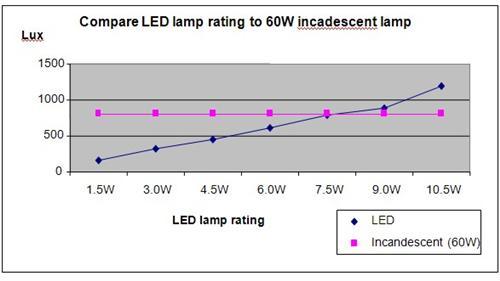
Results
It was observed that the 60W incandescent lamp provided the same brightness as a 7.5W LED lamp, showing that LED lamps provide the same brightness at a lower wattage and power consumption compared to the incandescent lamps.
The above results were then plotted onto a graph, a shown below.
| Lamp type | LED wattage and luminous intensity (lux) | ||||||
| 1.5W | 3.0W | 4.5W | 6.0W | 7.5W | 9.0W | 10.5W | |
| LED | 163 | 327 | 458 | 610 | 785 | 883 | 1187 |
| Incandescent (60W) | 812 | 812 | 812 | 812 | 812 | 812 | 812 |
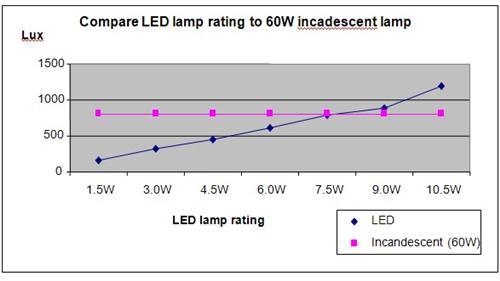
Conclusion
The hypothesis that the LED lamp would require less power to produce the same brightness as an incandescent lamp has been proven to be true.
LED lamps consume less power compared to an incandescent lamp in order to provide the same level of brightness. They also become less hot on the surface and have a longer lifespan. An incandescent lamp can last an average of 1,500 hours of running time compared to an LED lamp which can last up to 60,000 hours. However, the price of LED bulb is still many times higher than the incandescent bulb, although with time, the gap in price may narrow.
Also consider
Try to repeat the science fair project by comparing a florescent light with LED lamps.
The experiment can also be repeated by comparing the brightness of the LED lamp and incandescent lamp at different distances from the light source.
References
Incandescent light bulb - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incandescent_light_bulb
LED lamp - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LED_lamp
LED lights vs incandescents - http://www.ehow.com/about_5447908_led-lights-vs-incandescents.html

