| Complexity level: | 6 |
| Project cost ($): | 20 |
| Time required: | 1 hour to prepare, 1 hour for experiment |
| Material availability: | Easily found |
| Safety concerns: |
Hypothesis
Human hair will have the highest amount of static electricity.
Overview
Static Electricity
Static electricity is created when electric charges accumulate on the surface of a body. These electric charges will remain on the surface until they are discharged by contact with another surface.
All materials consist of atoms. These atoms have a nucleus containing neutrons and protons while the electrons are positioned outside the nucleus. The ability of an object to hold on to its electron or to release it, is determined by the object’s position in the triboelectric series.
When a certain matter is able to release its electron easily, it will become positively charged and fall on the positive side of the triboelectric series. On the other hand, if the matter captures electrons easily, it will become negatively charged and fall on the negative side of the triboelectric series.
Static charges are easily created by rubbing two insulating materials together. Friction between the two materials helps to generate static electricity. Through the rubbing process, electrons are transferred from the surface that releases electrons easily, to the surface captures electrons easily.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science fair project:
- 1 balloon
- 1 copper plate 200mm x 300mm
- 1 ground connection
- 1 jumper wire with crocodile clips at both ends
- Human hair
- 1 small piece of polyester cloth
- 1 carpet
- 1 small piece of cotton cloth
- 1 small piece of nylon cloth
- 1 ceramic tile
- A flat tray
- 1 ruler
- 1 sheet of paper
- 1 paper knife
MEL Physics — hands-on physics experiment kits delivered monthly — real experiments, not just reading. (Affiliate link)
See what’s includedProcedure
1. For this experiment, the independent variable is the type of material tested. The dependent variable is the number of pieces of paper picked up by the balloon. This is determined by simply counting the number of pieces. The constants (control variables) are the size of the balloon, the number of times the balloon is rubbed on the material tested and the weight of the paper bits.
2. The copper plate is connected to the ground connection using the jumper wire.
3. The sheet of paper is cut into 200 small pieces measuring 5mm x 5mm. The pieces are placed on the copper plate in order to ensure that all residual static electricity is discharged from paper. After that, the paper pieces are transferred to the flat tray.
4. The balloon is then inflated.The inflated balloon is also rolled across the copper plate to ensure that any residual static electricity is properly discharged before the experiment begins.
5. To begin the experiment, rub the balloon on the hair 5 times, in the same direction. Place the balloon on the cut pieces of paper. The paper pieces will be attracted to the balloon. Count the number of paper pieces sticking to the balloon and record the quantity in the table given below. Discharge the paper pieces on the copper plate and return them to the tray.
6. Discharge the balloon again by rolling it on the grounded copper plate.
7. Repeat procedures 5 and 6 by rubbing the balloon 5 times over the polyester cloth, carpet, cotton cloth, nylon cloth and ceramic tile in turn. Count the number of paper pieces picked up by the balloon and record the findings in the table below.
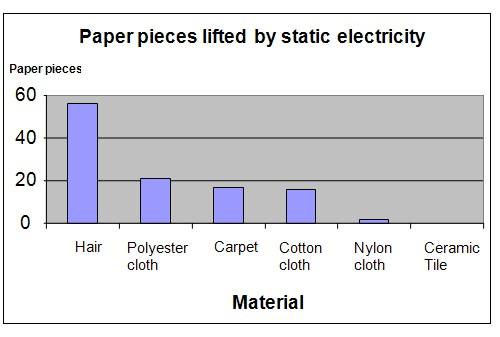
Results
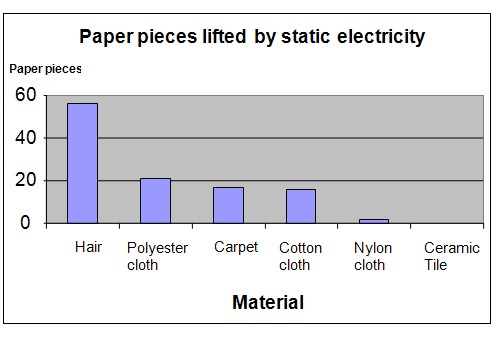
The results show that different materials have different amounts of static charges because different amounts of paper pieces stick to the balloons after it is rubbed against various materials. The balloon picked up the highest number of paper pieces after being rubbed against the hair.
|
Materials used to rub against balloon |
Number of paper pieces sticking to balloon |
|
Hair |
56 |
|
Polyester cloth |
21 |
|
Carpet |
17 |
|
Cotton cloth |
16 |
|
Nylon cloth |
2 |
|
Ceramic Tile |
0 |
The chart below represents the results of our observations.
Conclusion
The hypothesis that human hair has the highest static charge, is proven to be true.
Static electricity is more obviously present on days where humidity is very low. On days of high humidity, the charges are able to discharge through the moisture in the air. Static electricity can be harmful when working with electronics or in the presence of flammable gasses.
Also consider
The experiment can also be done using a comb instead of a balloon.
Try to compare the results by repeating the experiment to see how much the balloon will “pull” or attract a small stream of water flowing from the tap.
References
Static electricity - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_electricity
Static electricity - http://science.howstuffworks.com/vdg1.htm

